David Goyer, the renowned filmmaker behind the Blade trilogy, The Dark Knight, and Apple TV’s Foundation series, announced his latest project on Friday – a futuristic blockchain-driven universe named Emergence. Set...
Read moreScience
For the first time, researchers have used light to create a supersolid state—combining the rigidity of solids with the frictionless flow of superfluids. Led by CNR Nanotec in Italy, the breakthrough...
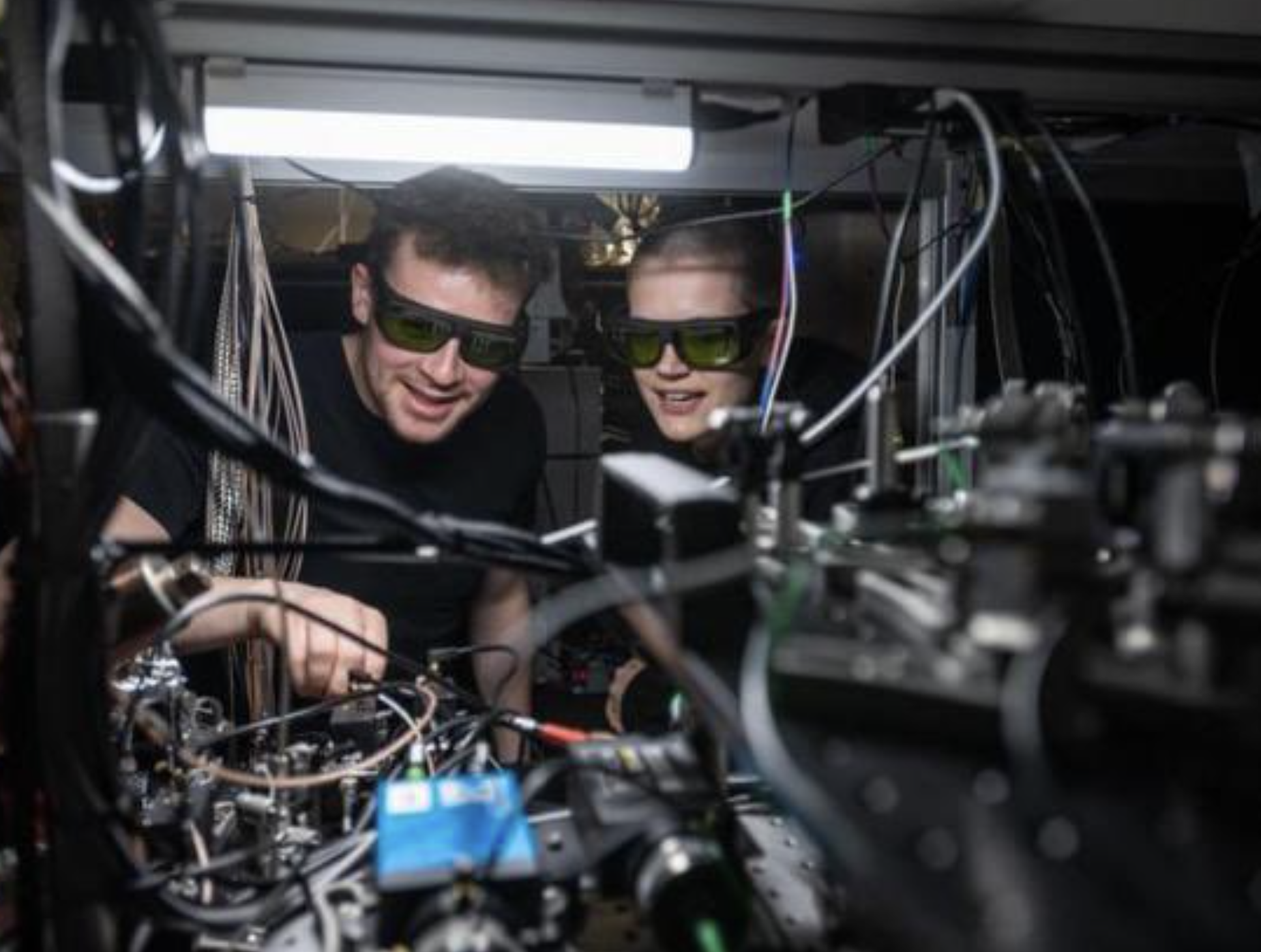
Read moreResearchers at the University of Oxford have made a groundbreaking advancement in quantum computing by developing a scalable quantum supercomputer capable of quantum teleportation. A key challenge in quantum computing has...
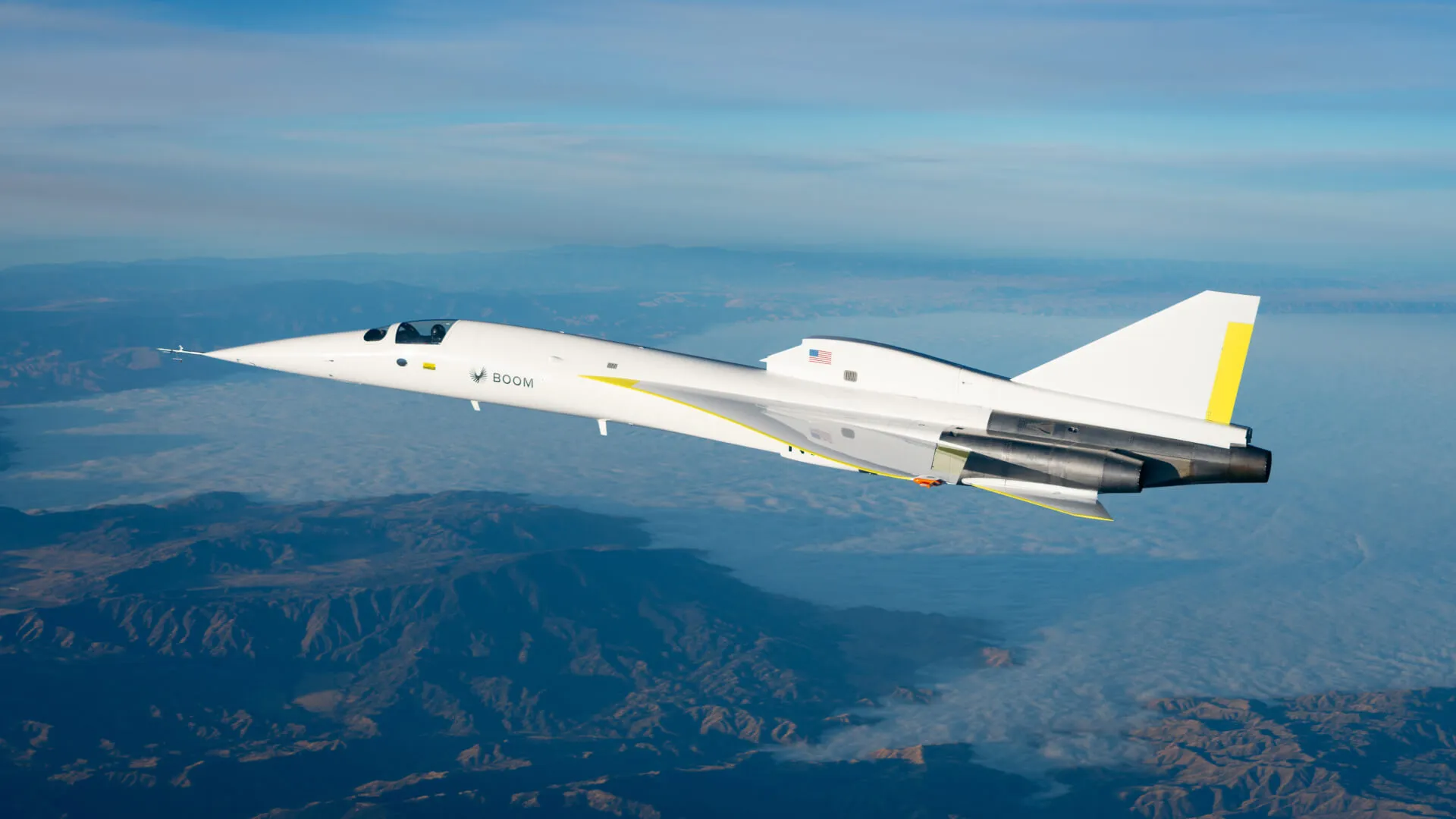
Read moreBoom Supersonic’s XB-1 Demonstrator Breaks the Sound Barrier, Ushering in a New Era of Air Travel Boom Supersonic has reached a historic milestone with its XB-1 demonstrator plane successfully breaking the...
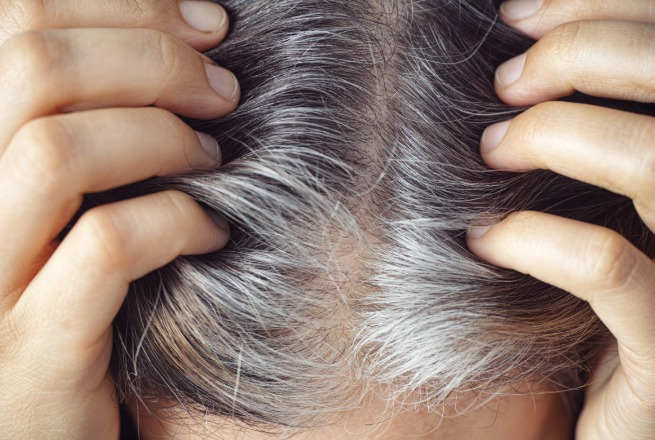
Read moreIn a recent study, mice treated with luteolin ”an antioxidant found in veggies like celery, broccoli, and onions ”kept their natural fur color, while untreated mice turned gray. The secret? Luteolin...
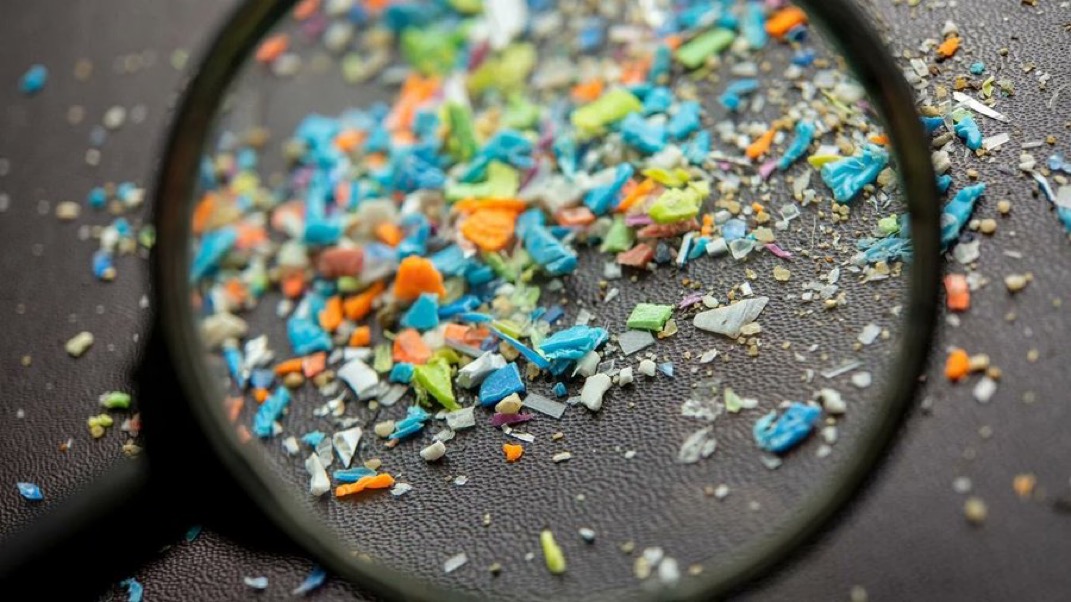
Read moreYou might already know about microplastics in our oceans and food, but here’s a new twist: they’re accumulating in our brains, too. A recent study has revealed astonishing levels of microplastics...
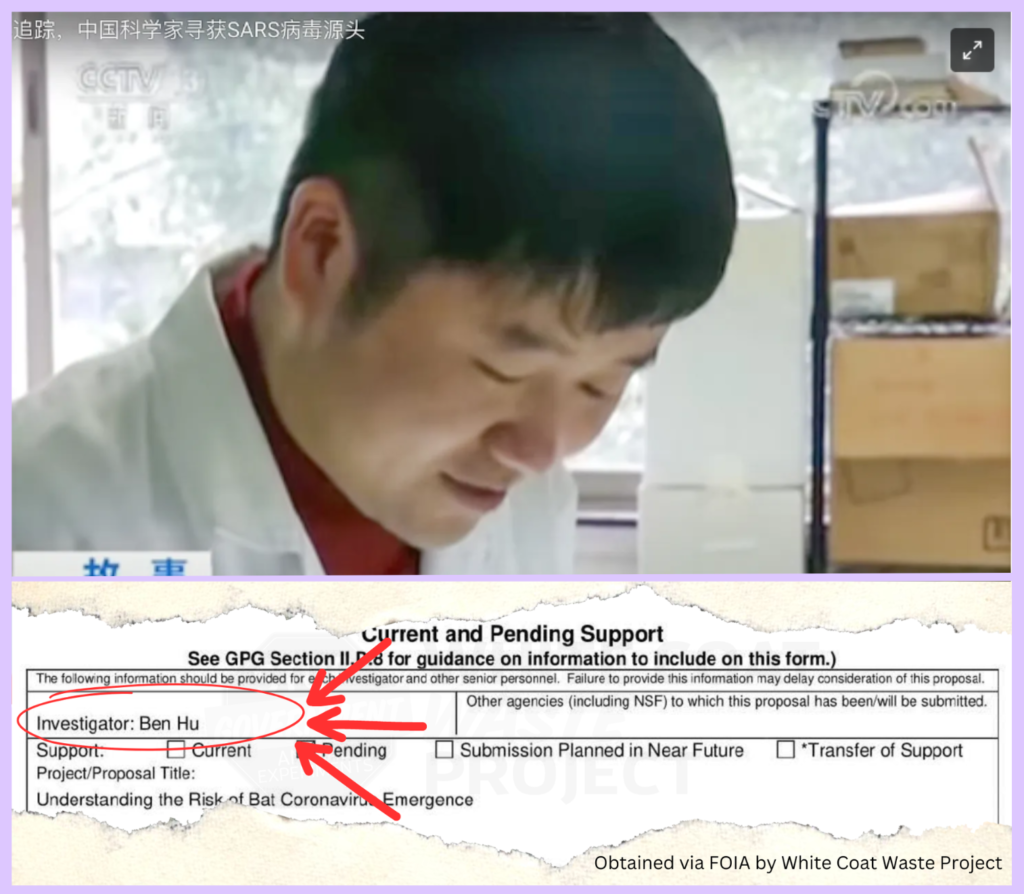
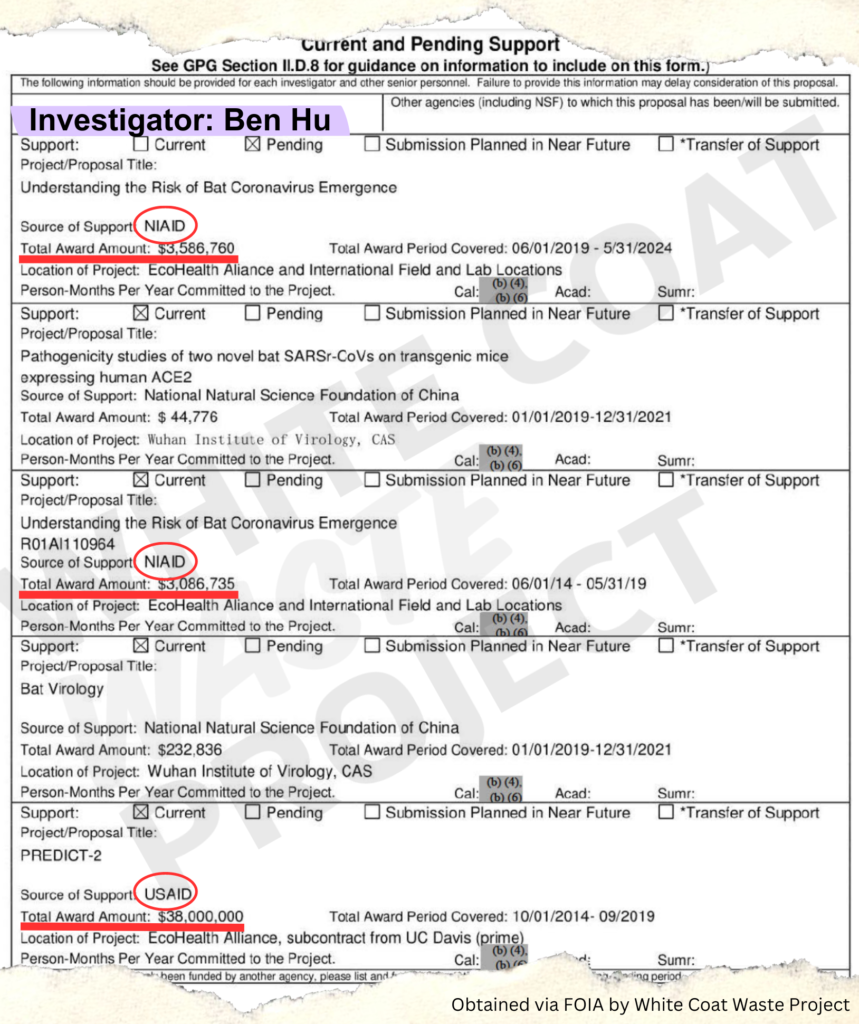
Read moreNew Findings Strengthen the Lab-Leak Hypothesis A recent investigation by the White Coat Waste Project (WCW) has uncovered new evidence linking U.S. government funding to Ben Hu, the Wuhan Institute of...
Read moreElon Musk’s Starlink is reportedly developing quantum communication technology, a groundbreaking advancement that could revolutionize internet security and speed. If successful, this technology would make Starlink’s network virtually unhackable, providing a...
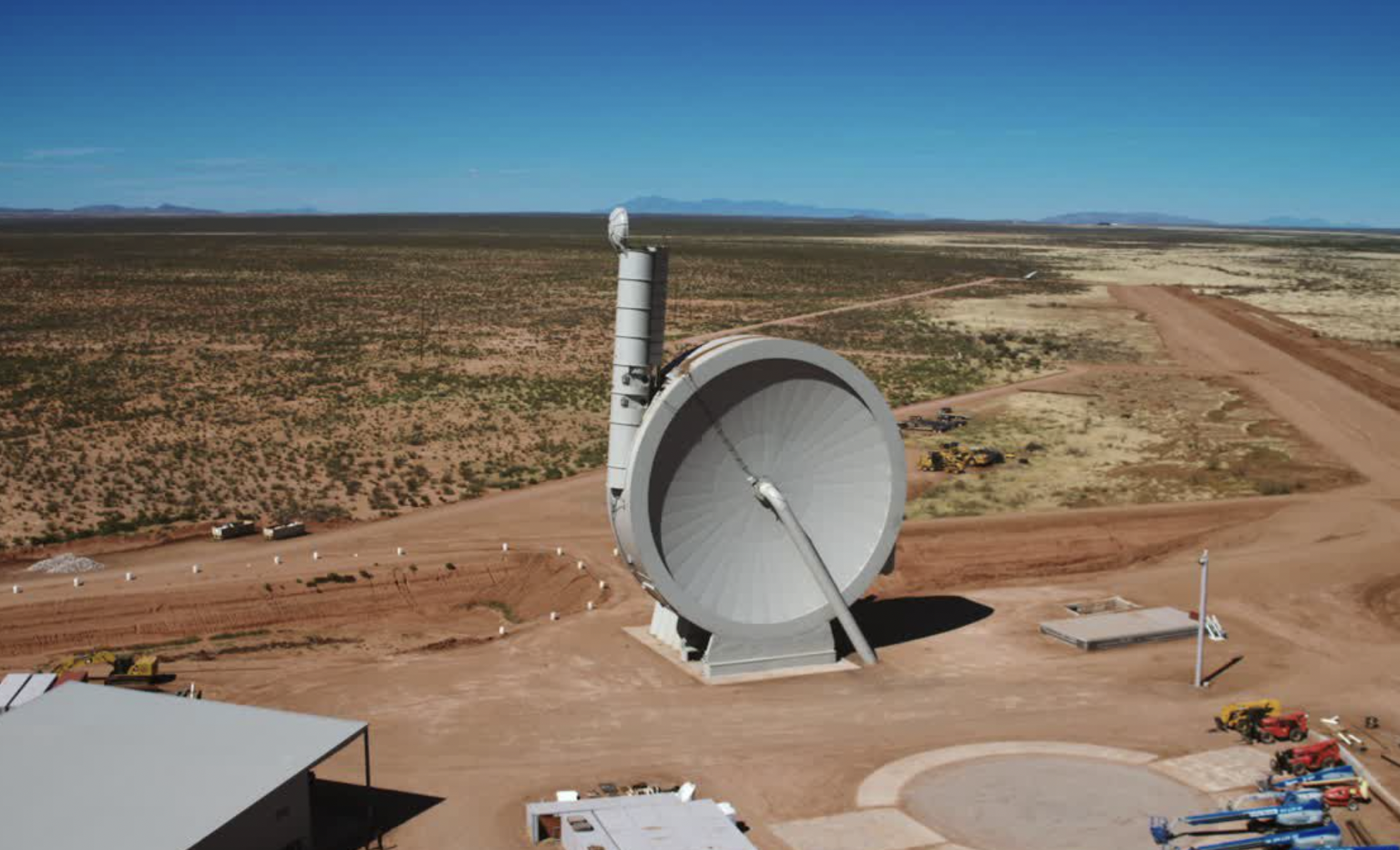
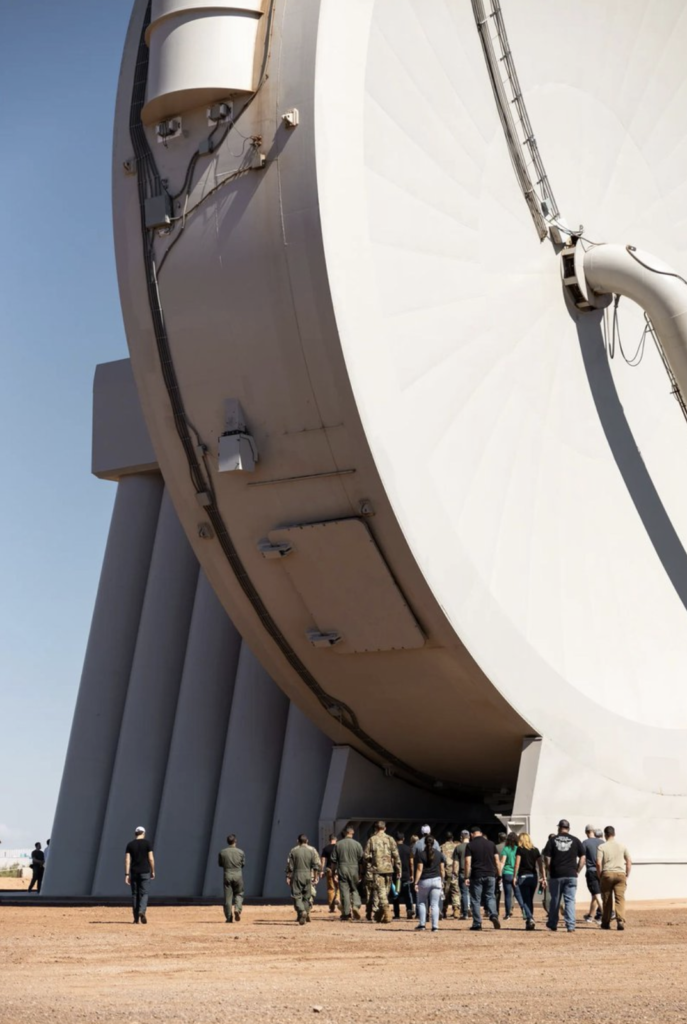
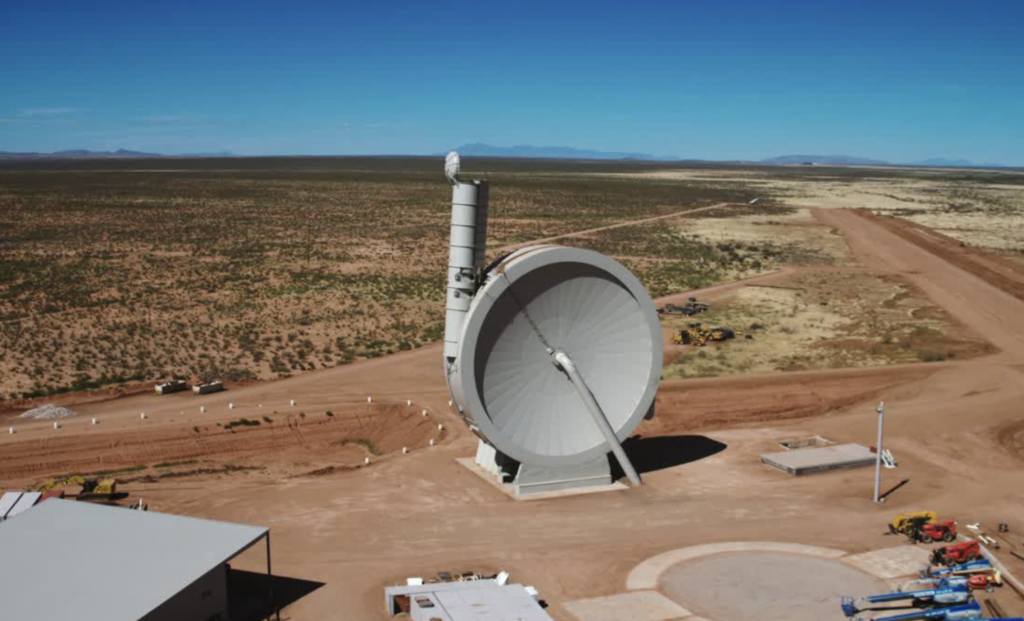
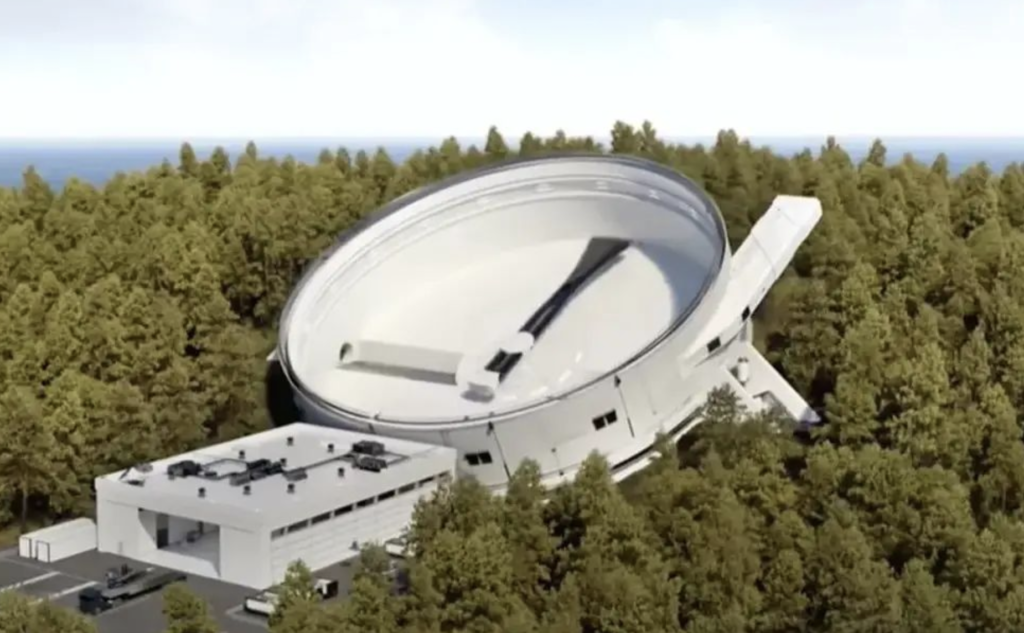
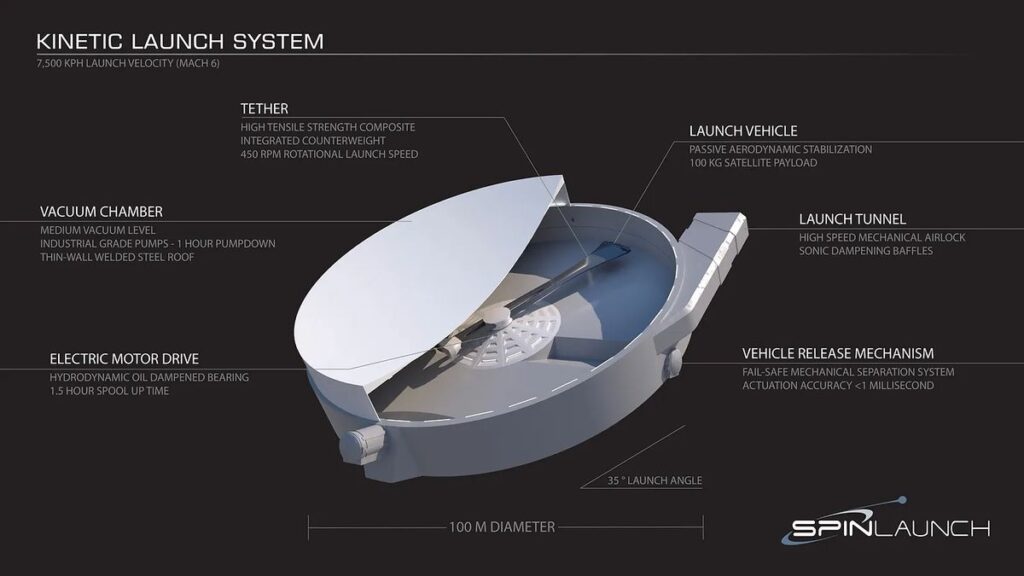
Read moreSpinLaunch is redefining spaceflight with a revolutionary catapult-like system that hurls satellites into orbit—completely rocket-free. Powered by a massive rotating arm, this electric-driven technology slashes costs, reduces emissions, and could transform...
Read moreTesla released a new RoboTaxi Self Cleaning robot – it has humor too!This means that the Robotaxi network will run 24/7. If you step out of a bar at 2 a.m....
Read more